I recently posted about my temporal chromatograms, and now I’d like to post about my temporal veterinary artwork!
I love using new media, so when I got the chance to be the first-ever artist in residence at a veterinary school in the United States (at the LSU School of Veterinary Medicine in 2022), I set myself the challenge of using veterinary chemicals, medicines, materials, and tools in each of my pieces created there. As far as I know, no one else has attempted to use either stains from clinical pathology and histology or veterinary chemicals and medicine as paint before. This meant I had no idea how archival any of the artwork would be.
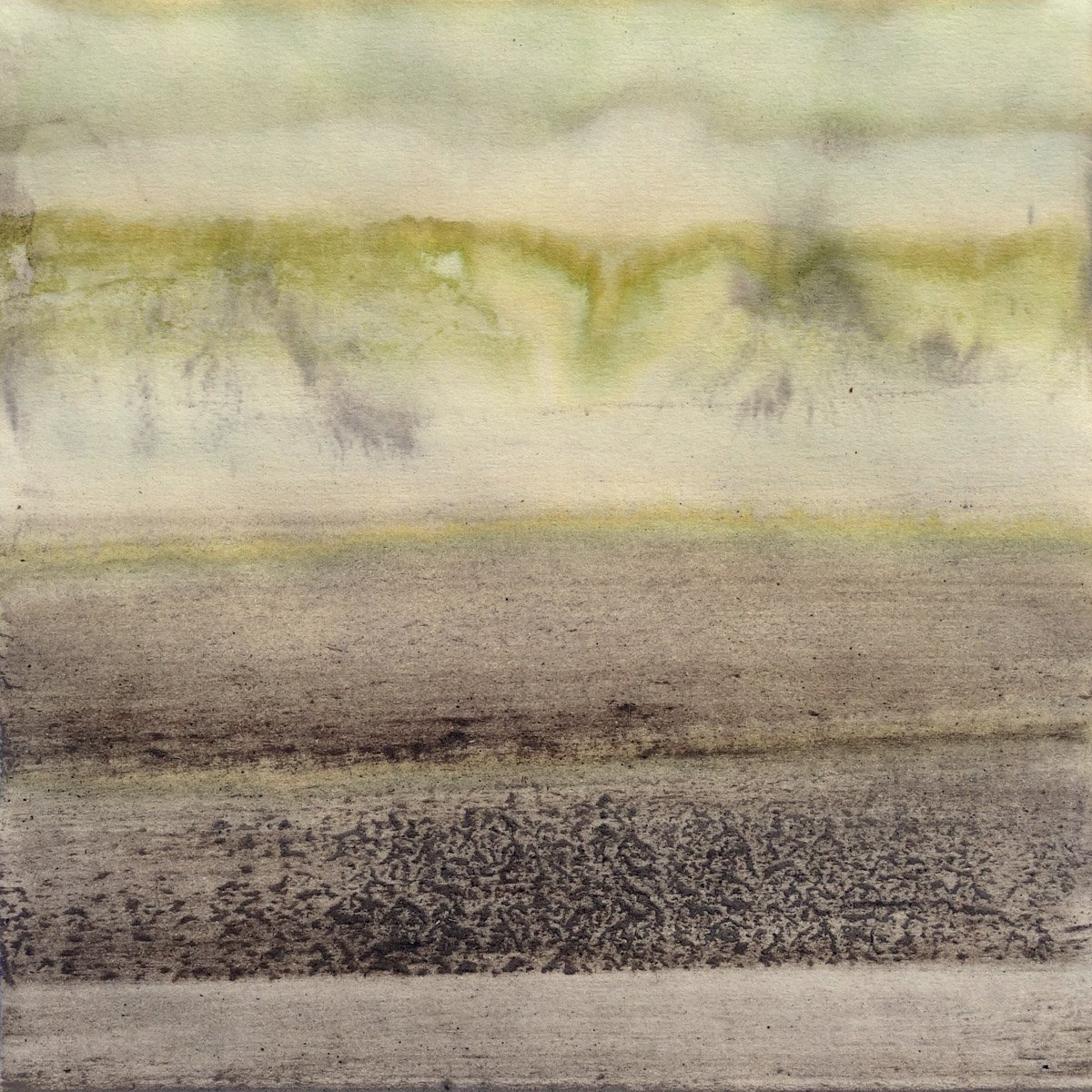
I soon found out that a lot of the veterinary stain and chemical pigmentation rapidly goes fugitive, which is a term we use in art when pigmentation bleaches out over time and/or with exposure to sunlight.
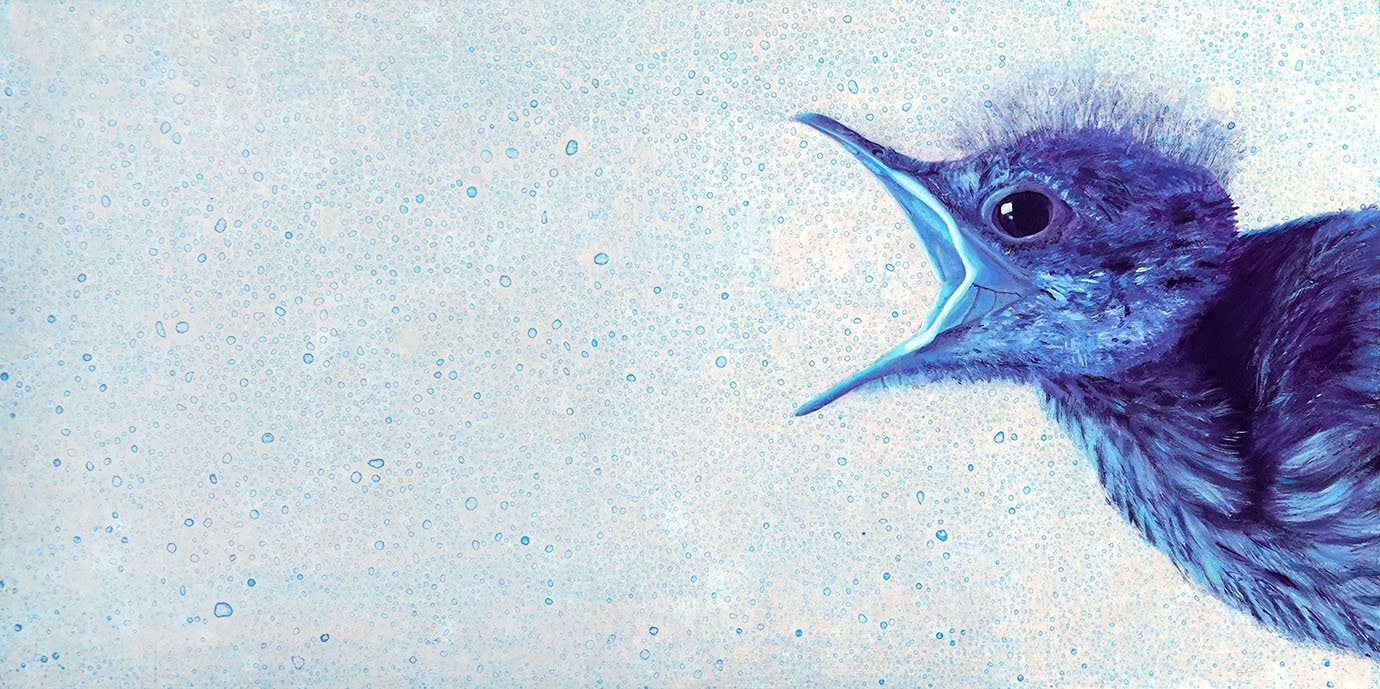
While a number of my paintings from my LSU Vet Med residency have therefore undergone a transformation, the most drastic one is that of Wild Card. Its background actively changed as I was painting it; the initial coloration was intensely cyan and purple. The cyan started disappearing within days, but the purple was more stable. However, the purple began to fade away in a matter of weeks. Here is a comparison of Wild Card on the day I finished the painting, and then another photo approximately a year-and-a-half later.
Again, I still find the latter result compelling. Fortunately, so did the viewers! The purplish background splotches went fugitive sufficiently quickly such that the version of the painting I exhibited in my solo show at LSU Vet Med had already mostly resolved to that of the above right image, and I sold the piece to a very nice emergency veterinarian who said he thought Wild Card had “aged like fine wine.” The novelty of how it will continue to age also interests us both!